Identifiers are the names that are given to various program elements such as variables, symbolic constants and functions.Variable or function identifier that is called a symbolic constant name.
Identifier can be freely named, the following restrictions.
- Alphanumeric characters ( a ~ z , A~Z , 0~9 ) and half underscore ( _ ) can only be used.
- The first character of the first contain letters ( a ~ z , A~Z ) or half underscore ( _ ) can only be used.
- Case is distinguishable. That is, word and WORD is recognized as a separate identifier.
- Reserved words are not allowed. However, part of an identifier reserved words can be included.
Here are the rules you need to know:
1. Identifier name must be a sequence of letter and digits, and must begin with a letter.
2. The underscore character (‘_’) is considered as letter.
3. Names shouldn't be a keyword (such as int , float, if ,break, for etc)
4. Both upper-case letter and lower-case letter characters are allowed. However, they're not interchangeable.
5. No identifier may be keyword.
6. No special characters, such as semicolon,period,blank space, slash or comma are permitted
Examples of legal and illegal identifiers follow, first some legal identifiers:
float _number;
float a;
int this_is_a_very_detailed_name_for_an_identifier;
The following are illegal (it's your job to recognize why):
float :e;
float for;
float 9PI;
float .3.14;
float 7g;
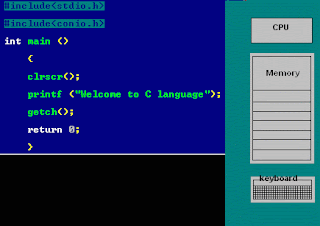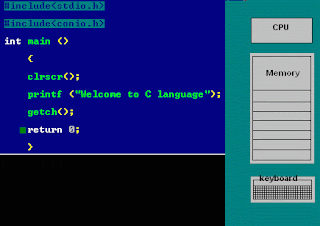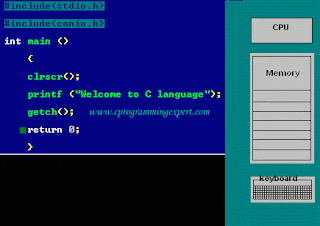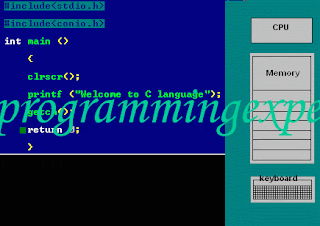
Example:
Click on following gif image: